Categories
Money money money...
Could we help you? Please click the banners. We are young and desperately need the money
Last updated: December 9th 2024
Categories: IT Knowledge
Author: Ian Walser
How to Identify Phishing Attacks: In-Depth Guide to Spotting Phishing Scams
Short introduction
In our increasingly digital world, phishing attacks have emerged as one of the most pervasive threats to online security. These attacks take many forms, aiming to deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and financial details. Understanding how to identify phishing attacks is crucial for everyone, from tech-savvy professionals to everyday users. This comprehensive guide will delve into the mechanics of phishing, helping you recognize potential threats and protect your data.
What is a Phishing Attack?
Phishing is a form of cybercrime where attackers impersonate legitimate entities to manipulate victims into divulging confidential information. This can happen through emails, websites, text messages, or social media, often appearing to come from trusted sources. The primary goal is to trick users into providing personal data or to install malware on their devices.
Why Phishing Attacks are Dangerous
Phishing attacks pose significant risks to both individuals and organizations. They can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and data breaches that compromise sensitive information. For organizations, the consequences can extend beyond financial loss, impacting reputation and customer trust. Understanding the dangers posed by phishing is the first step in developing effective defenses against these attacks.
Common Types of Phishing Attacks
Phishing can manifest in various forms. Here are some of the most common types:
- Email Phishing: The most widespread form of phishing, where attackers send mass emails that appear to be from legitimate companies, urging recipients to click on malicious links or provide personal information.
- Spear Phishing: Unlike general phishing attacks, spear phishing targets specific individuals or organizations. Attackers gather personal information about their victims to create convincing emails.
- Whaling: A type of spear phishing that targets high-profile individuals, such as executives or important decision-makers within an organization.
- Smishing: Phishing conducted through SMS text messages, where attackers may prompt victims to click on a link or call a fraudulent number.
- Vishing: Voice phishing, where attackers use phone calls to impersonate legitimate organizations, such as banks or government agencies, to extract sensitive information.
How to Identify a Phishing Attack: Top Signs and Red Flags
Identifying phishing attacks can be challenging, as attackers constantly refine their tactics. However, several common signs can help you recognize potential threats:
1. Suspicious Email Addresses
One of the most obvious signs of phishing is a suspicious email address. Phishing emails may come from addresses that resemble legitimate companies but contain slight variations or misspellings. For example, instead of support@amazon.com, the address might be support@amaz0n.com. Sometimes though, the email address looks very cryptic or is a "normal" gmail/yahoo/outlook email address. Always verify the sender's email address by checking the domain carefully.
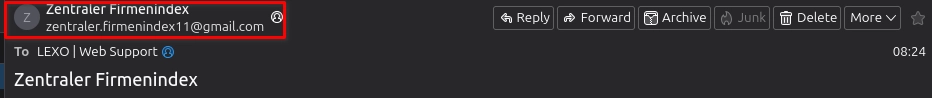
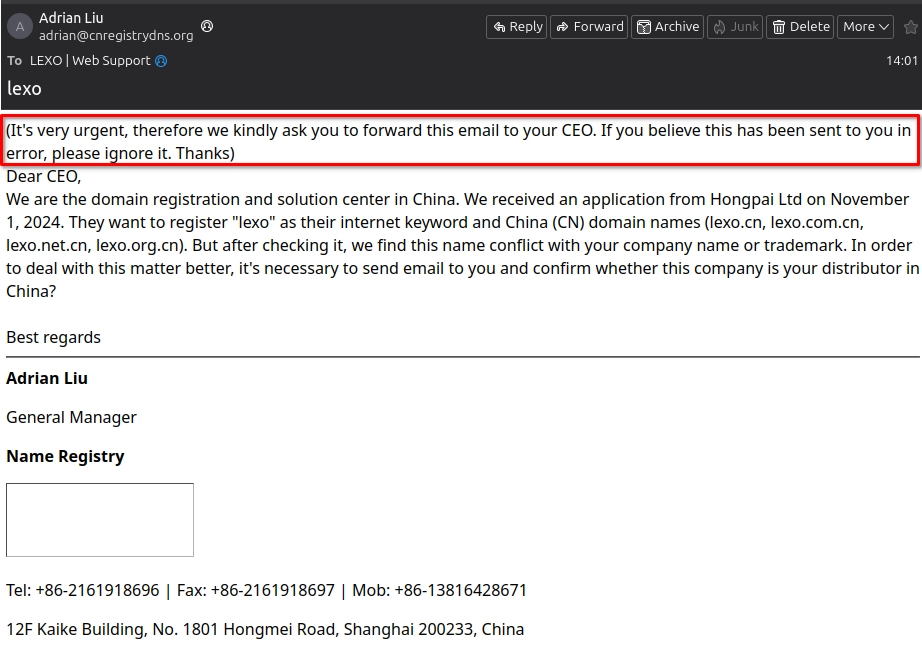
2. Urgent or Threatening Language
Phishing messages often create a sense of urgency, using language like “immediate action required” or “your account will be locked.” Legitimate companies typically avoid using threats to prompt quick responses. If an email sounds alarmist, it’s worth scrutinizing closely. This will look something like this:
3. Grammar and Spelling Errors
Many phishing emails contain noticeable grammar and spelling mistakes. Professional organizations usually have quality control measures to prevent such errors. Pay attention to emails that seem unprofessional or poorly written; these are often red flags.
4. Unfamiliar Links and Attachments
If a link seems suspicious or leads to an unfamiliar domain, do not click it. Instead, use link previews (hovering over links on desktops or holding down on mobile) to verify the URL before visiting the site. Additionally, be cautious with unexpected attachments, as they may contain malware.
5. Requests for Sensitive Information
Legitimate companies will never ask you to provide sensitive information, such as passwords or bank details, directly via email. Be wary of any message that requests confidential information, especially if it seems out of context.
6. Generic Greetings
Phishing emails often use generic greetings like "Dear Customer" instead of addressing you by name. Legitimate companies typically use personal salutations, especially if they have established a relationship with you.
7. Unexpected Prompts for Action
If you receive an unsolicited request to verify your account, update your payment information, or download an attachment, proceed with caution. Verify the request by contacting the company directly through official channels rather than using contact information provided in the email.
Visual Indicators of Phishing Emails
Visual cues can help identify phishing attempts. Here are common visual indicators to watch out for:
1. Fake Logos and Design
Phishing emails may use low-quality logos or designs that look “off” compared to official branding. For example, the logo may appear pixelated or distorted. Legitimate emails usually maintain consistent branding.
2. “Reply-to” and “From” Mismatch
Be cautious if the “From” address does not match the “Reply-to” address. This tactic is often used to redirect replies to a different email account, which may be controlled by the attacker.
3. Phishing Links Disguised as Buttons
Attackers often use buttons that look legitimate to disguise malicious links. These buttons may say things like “Verify Account” or “Update Password.” Always hover over the button to check the URL before clicking.
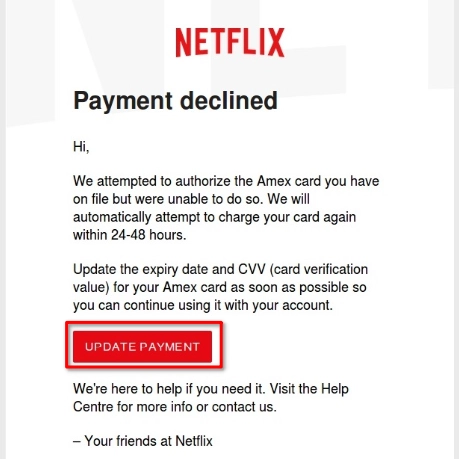
Practical Tips to Avoid Phishing Attacks
Preventing phishing attacks requires a combination of vigilance and technical measures. Here are some practical tips to help you stay safe online:
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enabling MFA adds an extra layer of security, making it more difficult for attackers to access your accounts, even if they obtain your credentials.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly updating your operating system, web browsers, and antivirus software is crucial. Outdated software can have security vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
- Install Email Filtering Software: Many email providers offer advanced spam and phishing filters that can help you avoid malicious emails. Use these tools to screen incoming messages.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Awareness is key. Educate yourself and your colleagues or family about phishing risks, and encourage them to report suspicious emails.
- Use a Password Manager: Password managers can help you generate strong, unique passwords and autofill them on legitimate sites, reducing the chance of entering credentials on a phishing site.
- Regularly Monitor Financial Statements: Keep an eye on your bank and credit card statements for any unauthorized transactions. Quick reporting can mitigate losses.
Comparison: Phishing Email vs. Legitimate Email
Here’s a comparison table highlighting differences between phishing emails and legitimate emails:
| Feature | Phishing Email | Legitimate Email |
|---|---|---|
| Sender's Email | Slight misspelling in domain | Correct domain and branding |
| Language Used | Urgent or threatening language | Professional and courteous tone |
| Links and Attachments | Links to unfamiliar websites | Links to official, recognizable domains |
Blackmailing and Email Spoofing
While writing this blog article we've received a suspicious email in our websupport inbox. Said email wasn't really a phishing mail but close to it. It was a so called "Blackmail" or "Ransommail". Some "master hacker" allegedly installed sophisticated spyware on our mobile devices and has "monitored us for the last few months". Here is how the email looked like:
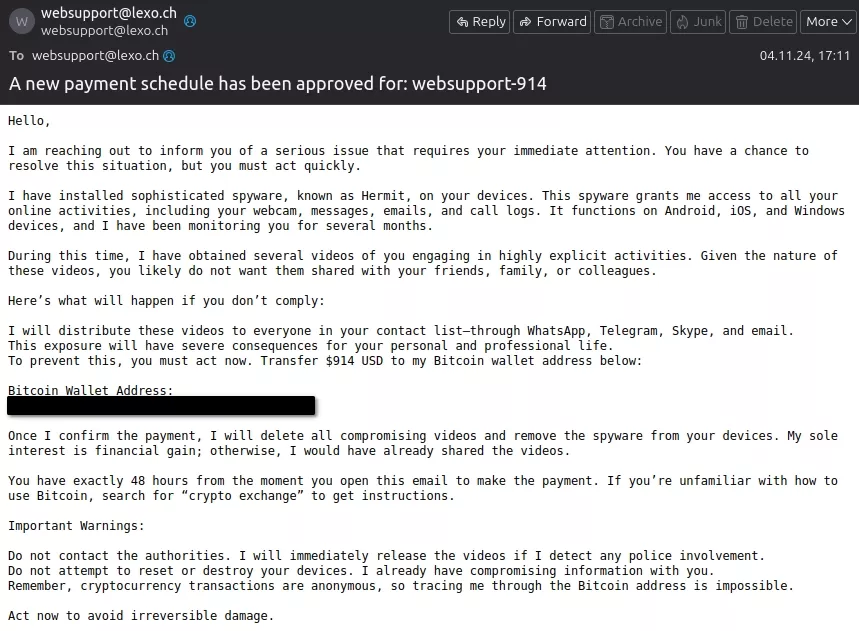
Something interesting here is following: The "sent from" and "reply to" email address got spoofed to look like one of our own. Now you might ask yourself "What exactly is (email) spoofing?". Well to put it short: "Spoofing is a type of cyberattack where a malicious actor disguises themselves as a trusted source to deceive individuals or systems. This can involve falsifying data, such as IP addresses, email headers, or websites, to make the communication appear legitimate. The goal is often to gain unauthorized access, steal sensitive information, or spread malware." (Source: ChatGPT)
Fun fact: You can also spoof hardware ID's of your pc components to evade gamebans (you didn't hear that from me 😉). If you want to read a little bit more about HWID spoofing you can read into this reddit thread.
How was the threat actor able to spoof the email even though we have an SPF enabled?
Before I go into too much detail lets look at what an SPF is first: "SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is an email authentication method that helps verify whether a mail server is authorized to send emails on behalf of a specific domain. It works by checking the domain's SPF record, a DNS entry that lists IP addresses and servers allowed to send mail for that domain. If the sending server's IP isn't on the list, the email can be flagged or rejected to prevent spoofing and phishing attempts." (Source: ChatGPT)
Now back to my original question: How was the threat actor able to spoof the email even though we have an SPF enabled?
Even with SPF enabled, spoofing the "FROM" field in an email is still possible because SPF only checks the "MAIL FROM" field (also called the envelope sender) used for technical routing, not the "FROM" address that recipients see in their email client. Attackers can exploit this by using a domain they control (or one without SPF) in the "MAIL FROM" field, allowing the email to pass the SPF check. They can then set the visible "FROM" field in the email headers to display any address they want, making it appear as if the email is from a trusted source. Since SPF does not enforce alignment between the "MAIL FROM" and the visible "FROM" address, the recipient may see a spoofed sender even though the email passed SPF. This is why DMARC, which enforces alignment between these fields, is often recommended alongside SPF for more robust email authentication. (Source: ChatGPT)
If you receive a similar email like this one analyze it very carefully and don't panic. Because that is the exact thing these threat actors are trying to achieve. If you can not identify if an email is legit, ask a friend or try to find answers on the internet. Something very important here is the fact that most of the time these threat actors haven't even infected your devices with their spyware. They are simply just trying to cause a fuzz that hopefully leads to victims giving them money out of panic. But there is still a possibility that you actually have spyware on your system. So whenever stumbling over such an email, always double check if you actually downloaded something fishy or strange from the internet. If you haven't you're 99% good. If you have though it's best to analyze everything in detail or consult an expert who will be able to help you out a bit more.
I really have to say that this "Blackmail" is one of the better ones. They at least made the effort to not use some random cryptic email. To end this whole section about blackmailing and email spoofing off, I just want to say one thing. If you're not sure about the legitimacy about an email, carefully analyze the email or consult an expert. And most importantly: Don't panic.
Conclusion
Phishing attacks are evolving, but by recognizing common signs and understanding the differences between legitimate and phishing emails, you can protect yourself from these schemes. Regular vigilance and adherence to best practices, like enabling multi-factor authentication, go a long way toward maintaining online safety. Educate yourself, stay aware, and share this information with others to contribute to a safer online environment.
