Categories
Money money money...
Could we help you? Please click the banners. We are young and desperately need the money
How to Find When Google First Indexed a Website: The Hidden 'as_qdr' Parameter Trick
How to Find When Google First Indexed a Website: The Hidden 'as_qdr' Parameter Trick
Ever wondered when Google first discovered and indexed a particular website? Whether you're an SEO specialist, digital researcher, or just curious about the history of websites, there's a lesser-known Google search parameter that can help you uncover this information. In this guide, we'll explore how to use the 'as_qdr' parameter to discover when websites first appeared in Google's index.
What is the 'as_qdr' Parameter?
The 'as_qdr' parameter is a special URL parameter that you can add to Google search queries to filter results based on when they were first indexed. While Google typically uses this parameter for time-based filters (like past year, past month), it can also reveal historical indexing information when used with specific values.
How to Use the Parameter
Using this trick is surprisingly simple. Here's how to do it:
- Start with your regular Google search URL
- Add &as_qdr=y15 to the end of the URL
- The number after 'y' represents the number of years to look back
Example Usage
Here's how to use it with specific examples:
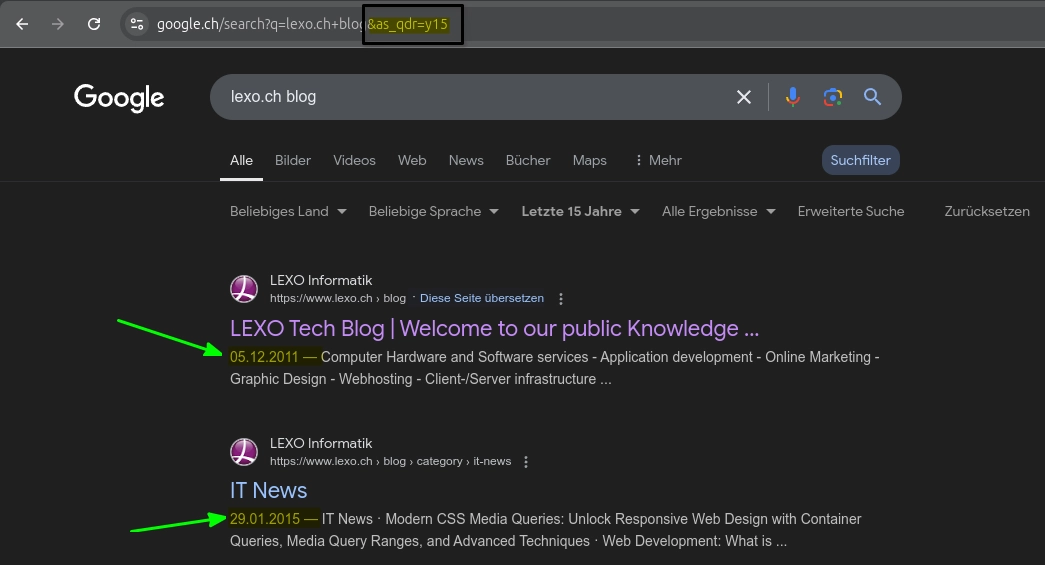
https://www.google.ch/search?q=site:lexo.ch/blog&as_qdr=y15This searches for indexed pages from lexo.ch/blog going back 15 years.
For a global search without the site: operator:
https://www.google.ch/search?q=lexo.ch+blog&as_qdr=y15Advanced Usage Tips
Adjusting the Time Range
You can modify the number after 'y' to change the time range:
- y5 - Look back 5 years
- y10 - Look back 10 years
- y20 - Look back 20 years
Comparing Different Search Methods
| Feature | as_qdr Parameter | Wayback Machine | WHOIS Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shows First Index Date | Yes | Partial | No |
| Historical Content Access | No | Yes | No |
| API Available | No | Yes | Yes |
Limitations and Considerations
While this method is useful, it comes with some limitations:
- The results may not always show the exact first indexing date
- Google's index data might not go back as far as you need
- Results can vary depending on your location and Google domain
- Some pages might have been reindexed, affecting the historical data
Practical Applications
This technique can be particularly useful for:
- SEO Research: Understanding when competitors' content was first indexed
- Content Analysis: Tracking the evolution of websites over time
- Digital Forensics: Investigating when specific information appeared online
- Competitive Analysis: Understanding the history and growth of competitor websites
Best Practices for Usage
To get the most accurate results:
- Start with a broader time range and narrow it down
- Use specific site: operators for more precise results
- Compare results across different time ranges
- Cross-reference with other tools like the Wayback Machine
Combining with Other Search Operators
The 'as_qdr' parameter can be combined with other Google search operators for more powerful searches:
site:example.com inurl:blog &as_qdr=y15
site:example.com filetype:pdf &as_qdr=y15
site:example.com intitle:"keyword" &as_qdr=y15Conclusion
The 'as_qdr' parameter is a powerful tool for understanding the historical presence of websites in Google's index. While it has its limitations, when used properly, it can provide valuable insights for SEO professionals, researchers, and anyone interested in the evolution of web content over time.
Remember to use this tool as part of a broader research strategy, combining it with other resources like the Wayback Machine and WHOIS data for a complete picture of a website's history.
